India is one of the largest resource-rich countries in the world with diverse natural resources. Mining plays a crucial role in the country’s economy, providing ener gy, industry and export potential. In this article, we take a detailed look at the major types of minerals, mining regions, and the challenges and prospects of the industry.
The role of the extractive industry in the Indian economy
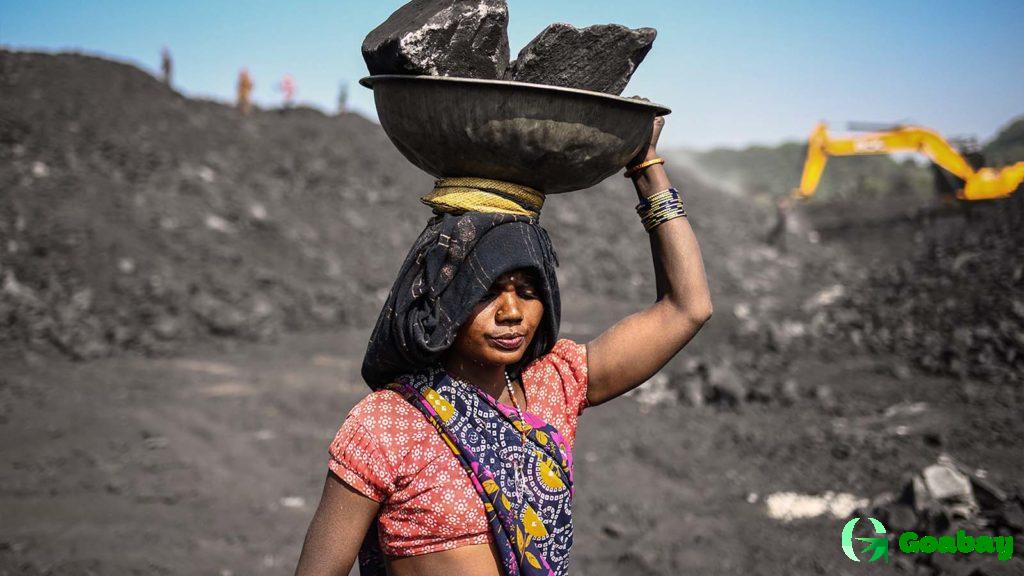

Mining accounts for about 2.5% of India’s GDP (including oil and gas). It provides jobs for millions of people, contributes significantly to regional development and meets domestic demand for raw materials for energy, construction and industry.
India is the world’s 2nd largest coal producer, 5th largest iron ore producer, and a leader in the production of bauxite, limestone and manganese.
Main types of minerals

- Coal. India is the second largest producer of coal after China. The main coal basins are Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Iron ore. Major deposits: Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, Goa. Iron ore is exported to China, Japan, and South Korea.
- Bauxite. India has large reserves of bauxite used for aluminum production. The main deposits are in Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, and Gujarat.
- Copper ores. Deposits are located in the states of Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan. Uses: manufacture of electrical engineering and alloys.
- Limestone. Widely used in construction and cement production. Main mining regions: Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu.
- Gold. The main deposits are located in Karnataka (Kolar district). Gold production is limited, and the country actively imports the metal.
- Oil and natural gas. The main oil and gas basins are Gujarat, Rajasthan, Andaman Islands, offshore platforms in the Arabian Sea.
- Rare earth elements. Used in production of high-tech electronics. Main deposits: Kerala, Tamil Nadu.
Geography of mineral extraction
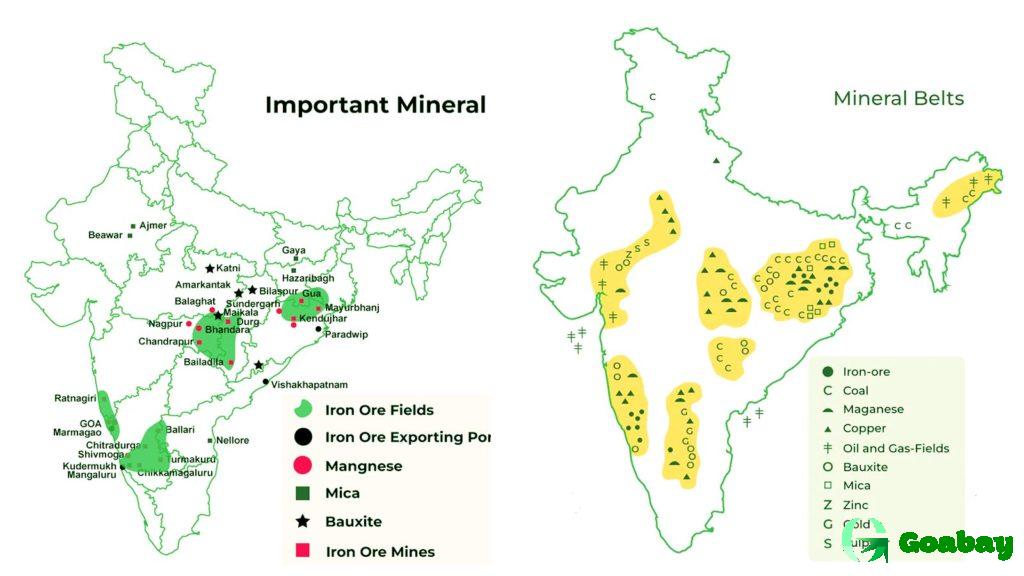
India is one of the largest countries in the world in terms of mineral reserves and production. The division of the country into mining and geological zones helps in efficient resource management. Here are the major zones and their riches:
- Central India Zone. The main resources are iron ore, coal, and manganese. The region plays a key role in the steel and energy industries.
- East India. A leader in coal and bauxite mining. The largest coal basins of the country are located here.
- Western India. Main minerals: oil, gas, limestone. The region is important for cement production and energy resources.
- South India. Rich in gold and granite. The region is famous for mining jewelry metals and materials for construction.
This unique geography provides India with leadership in the production of many strategically important resources needed for both domestic and international markets.
Challenges for the extractive industry

The mining industry in India, despite its strategic importance to the economy, faces a number of serious problems:
- Mining causes deforestation, pollution of water bodies and soil. Public and environmental organizations are mounting pressure to shift to more sustainable practices.
- Outdated mining methods are still used in some regions. This leads to low productivity, increased costs and additional environmental impacts.
- Local communities often protest against mining companies’ activities, which can destroy their traditional way of life and violate their land rights.
- The process of obtaining licenses and approvals is often protracted, slowing the start-up of new projects. Strict laws make mining development more difficult, especially in environmentally sensitive areas.
Addressing these challenges requires a balance between economic interests, technology and social and environmental responsibility.
Mining Development prospects

The introduction of modern mining and processing technologies will help increase productivity and reduce environmental damage. The Indian government plans to pay more attention to environmental remediation and land reclamation. meanwhile, it is actively attracting foreign investment to explore new deposits and develop infrastructure. In the face of global competition, India is striving to take a leading position in the production of rare earth metals, which are in demand in high-tech industries.
Mining plays a key role in the development of the Indian economy. Despite environmental and social challenges, the country continues to be one of the largest suppliers of raw materials in the world. The introduction of modern technologies, transition to sustainable development and international cooperation will be the basis for further growth of this important industry.




